ARB Medications: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your blood pressure stays too high, your heart and kidneys pay the price. That’s where ARB, a type of blood pressure medication that blocks angiotensin II receptors to relax blood vessels and reduce strain on the cardiovascular system. Also known as angiotensin receptor blocker, it works differently than ACE inhibitors but often delivers similar results with fewer side effects like coughing. ARBs are one of the most common first-line treatments for hypertension, especially for people who can’t tolerate ACE inhibitors.
These drugs don’t just lower numbers on a gauge—they protect your organs. Studies show ARBs reduce the risk of kidney damage in diabetics, lower heart failure hospitalizations, and even slow the progression of certain types of heart disease. They’re often prescribed alongside other medications like diuretics or calcium channel blockers, but many patients take them alone. Unlike beta-blockers that slow your heart rate, ARBs target the hormone system that tightens your arteries. That makes them especially useful for people with metabolic syndrome, obesity, or a family history of early heart disease.
Related to ARBs are other cardiovascular drug classes like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers—but ARBs stand out because they don’t cause that dry, annoying cough that many people get with ACE inhibitors. They’re also preferred for patients with chronic kidney disease, especially those with protein in their urine. If you’ve been told your blood pressure is high and your doctor says "try an ARB," it’s not just a random choice. It’s based on how your body handles stress, how your kidneys are functioning, and whether you’ve had reactions to other drugs.
What you’ll find below is a collection of real, practical guides written for people who take these meds—or are considering them. You’ll see comparisons between ARBs and other blood pressure drugs, insights into side effects, and even how they interact with other conditions like diabetes or heart failure. These aren’t marketing pages. They’re clear, no-fluff breakdowns from people who’ve lived with these drugs, their benefits, and their risks. Whether you’re just starting out or have been on an ARB for years, there’s something here that helps you understand why it’s working—or why it might not be.
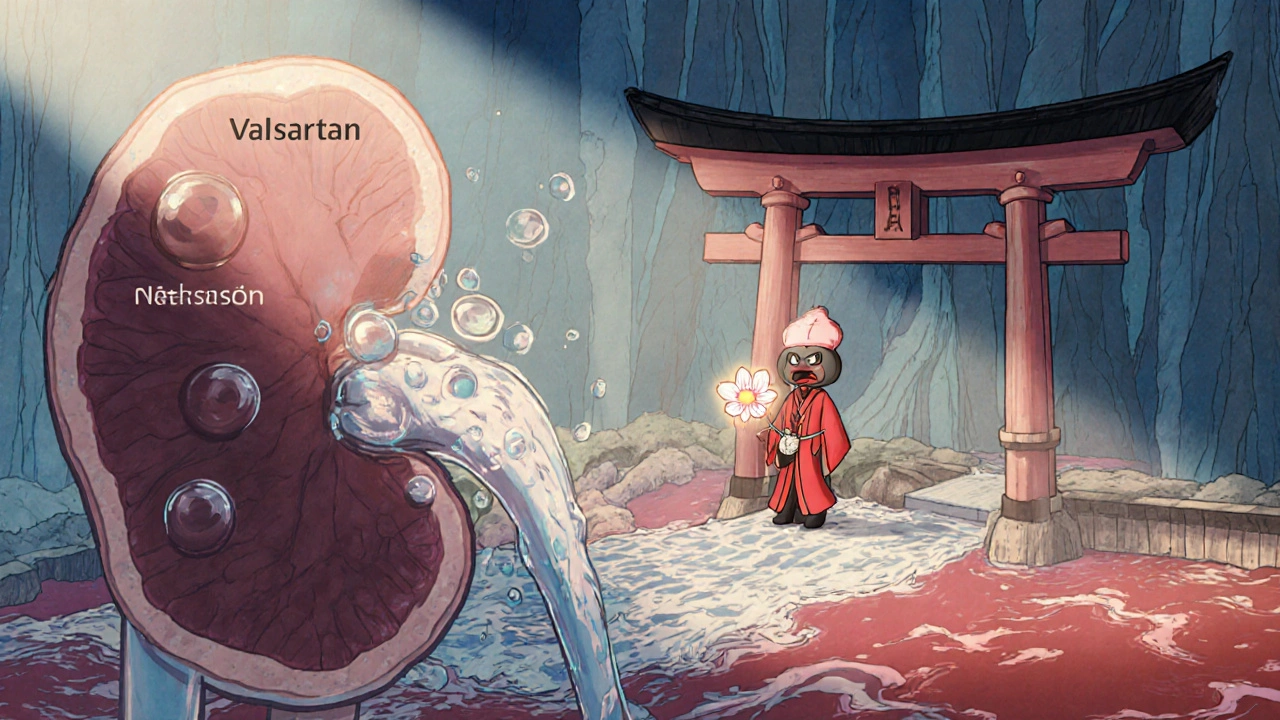
Valsartan’s Role in Preventing Heart Attacks and Strokes - What the Evidence Shows
Explore how Valsartan works, its clinical evidence for heart attack and stroke prevention, and practical tips for patients considering this ARB medication.