Enzyme Therapy Explained: What It Is and How It Works
If you’ve ever felt bloated after a dairy latte or struggled with low energy, enzymes might be the missing piece. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in your body – mainly breaking down food so you can absorb nutrients. When your body can’t make enough on its own, adding them from outside is called enzyme therapy.
What Exactly Is Enzyme Therapy?
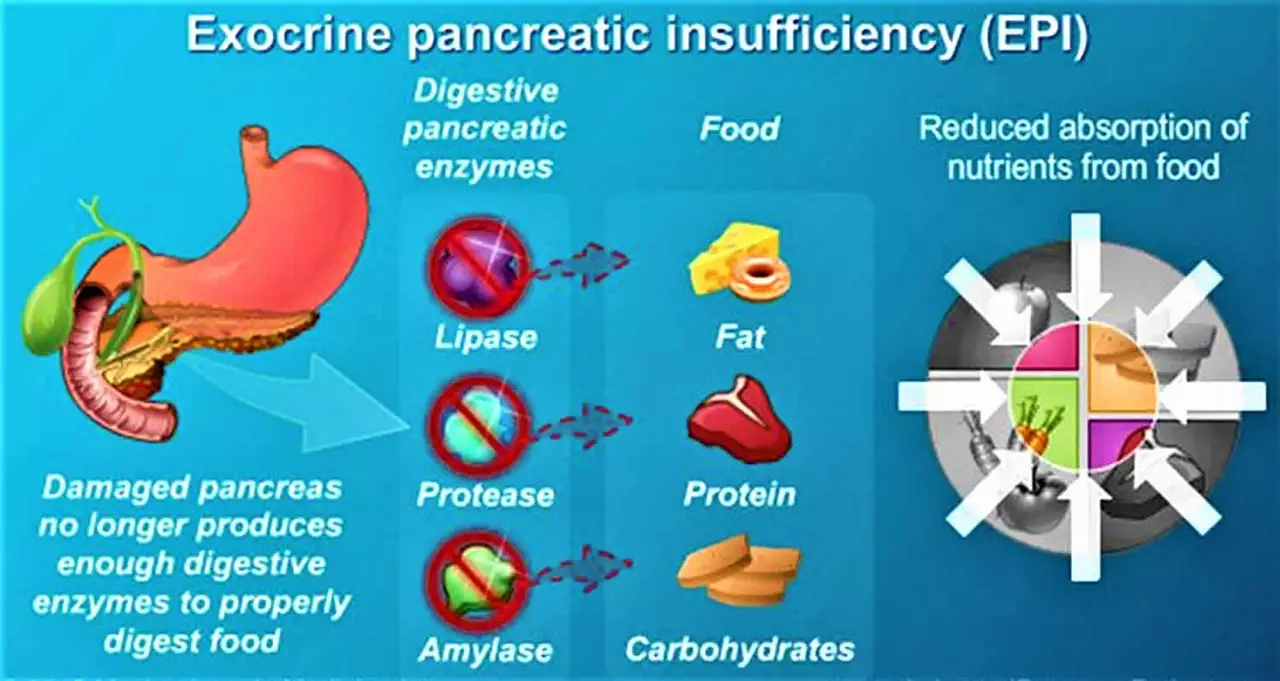
There are two main flavors of enzyme therapy. The first is digestive enzymes, which help break down carbs, fats, and proteins. You’ll see these in pills labeled “lipase,” “amylase,” or “protease.” They’re popular for lactose intolerance, pancreatic insufficiency, or just a heavy meal.
The second type is enzyme replacement therapy (ERT). This is a prescription treatment for rare genetic disorders like Gaucher disease or Pompe disease. In ERT the missing enzyme is delivered by IV so it can reach organs that need it.
How to Use Enzyme Supplements Safely
Here’s a quick checklist before you pop a capsule:
- Know your need. If you’re targeting digestion, pick a broad‑spectrum blend or one specific to your issue (e.g., lactase for dairy).
- Check the dosage. Start low – often half a tablet with meals – and watch how you feel. Most labels give a range; stick within it.
- Buy from reputable sources. Look for pharmacies that require a prescription or at least list batch numbers, expiration dates, and third‑party testing. Our site’s guide to safe online pharmacies can help you spot legit sellers.
- Watch for interactions. Enzymes can affect the absorption of certain drugs (like antibiotics). If you’re on meds, ask your doctor or pharmacist before adding enzymes.
- Store properly. Keep them dry and away from heat. Some enzyme blends lose potency after a year, so note the “best by” date.
If you have a diagnosed condition that requires ERT, never try to DIY it with over‑the‑counter products. Those enzymes are designed for the gut, not for fixing genetic deficiencies. Always follow your specialist’s prescription and schedule.
Real‑World Benefits You Might Notice
People who use digestive enzymes often report less gas, smoother digestion, and more steady energy after meals. For those on ERT, the therapy can slow disease progression, improve muscle strength, and reduce organ enlargement. Results vary, so keep a simple journal: note what you ate, which enzyme you took, and how you felt afterward.
Bottom line: Enzyme therapy can be a handy tool when your body’s own enzymes fall short. Choose the right type, stick to trusted sellers, and pair it with good nutrition for best results. Got questions about where to buy safe supplements? Check our “How to Find Legitimate Canadian Online Pharmacies” guide – it walks you through credentials, encryption, and pharmacist access so you can shop with confidence.
Ready to give enzymes a try? Start with a low dose at your next meal, track the outcome, and adjust as needed. If symptoms persist or you suspect a deeper condition, book an appointment with a healthcare professional. Enzyme therapy works best when it’s part of a broader plan that includes diet, lifestyle, and medical oversight.
The Role of Enzyme Therapy in Addressing a Lack of Enzymes and Related Health Issues
Enzyme therapy has become increasingly important in treating health issues related to a lack of enzymes in our bodies. As a blogger, I've discovered that this therapy helps replenish essential enzymes, improving digestion and overall health. By breaking down food particles, enzyme therapy can alleviate symptoms like bloating, gas, and indigestion. It's fascinating to learn how this therapy can also boost our immune system and reduce inflammation. In conclusion, enzyme therapy plays a crucial role in addressing enzyme deficiencies and related health issues, ultimately improving our quality of life.